His prolonged
productive cough, hemoptysis, weight loss, and cavitary lesions on CXR is
consistent with pulmonary tuberculosis
2-c
He has signs of
possible abuse on physical exam.
I know in the ER they
typically do C. and it sounds best. You wouldn’t want to confront the patient’s
family because you don’t know for sure.
You wouldn’t just remove him because you don’t know who is actually
abusing him or if he even is. Social services could look into it and something
can be done without jumping to conclusions and blaming people
3-b
Sudden death due
to pulmonary embolism. DVT from being bedridden was source of emboli.
Being bedridden puts her at risk for
DVTs. Cancer in general can create a
procoagulable state. With two risk factors for DVT it seems like the most
likely diagnosis. Additionally it
correlates well with the clinical scenario of a sudden onset of dyspnea and
chest pain and the quick death.
Virchow’s Triad:
1. stasis
2. hypercoagulability
3. endothelial damage
4-e
Symptoms are
consistent with GERD which is due to malfunction of LES
Esophagitis is associated with reflux, HSV-1, CMV, candida, or chemical
ingestion.
A. Cockscrew
esophagus.
B Failure to relax is achalasia and results in uncoordinated
peristalsis, dysphagia,à
Bird’s Beak. Also increased risk of carcinoma.
C. Cause of peptic ulcer
disease, gastritis, increased risk of cancer, but is not really associated with
esphagael problems.
GERD is also
associated with regurg upon laying down and after meals. People with
GERD typically have prolonged or
inappropriate relaxation of their LES
5-b
with decreased oxygen available there is first diminished oxidative
phosphorylation in the mitochondria with subsequent decrease in ATP
.
Sudden occlusion of CA aerobic or mitochondrial metabolism shifts to anaerobic
glycolysis (depleated glycogen granules) within seconds. Mitochondrial metabolism is most effected and
a oxidative phosphorylation stops resulting in decrease in ATP which stimulated
glycolysis. Decreased ATP results in
Na/K atpase shut down which leads to cell swelling.
6-a
Symptoms consistent
with Parkinson’s Disease
7-i
the patient’s chronic HTN -> LVH -> S4
8-e
7-i
the patient’s chronic HTN -> LVH -> S4
8-e
Increased enzyme activity of
phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase is responsible for purine overproduction
and gout.
9-a
The symptoms described are characteristic of myotonic dystrophy. It is an autosomal dominant trinucleotide repeat disorder. The disease exhibits a highly variable age of onset which decreases with successive generations. Thus, the disease shows at an earlier age in successive generations which is a phenomenon known as anticipation
10-e
low C peptide due to insulin abuse; low blood glucose should suppress insulin in normal pt
Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by treated diabetes patients and rarely occurs in insulin producing tumours. Decreased C-peptide suggests inability to make insulin (such as diabetes Type I.)Insulinoma would have hypoglycemia, high insulin levels, and high C-peptide levels. Type I diabetes would have decreased insulin and c-peptide. The high insulin and low C-peptide (precursor to insulin)suggests that she is ingesting insulin.psych consult?
11-d
At high stringency duplexes form only between strands with perfect one-to-one complementary. Low stringency allows annealing between strands with some degree of mismatch between bases.
So when they renature they reanneal together. High stringency means that the conditions are strict and they won’t accept bad mismatches. So mismatched dna hybridization will be prevented
12-e
mother has oligohydramnios which can be due to problems with development of kidneys or urinary tract which causes little urine production and leads to low amniotic fluid level Baby’s renal system produces amnionic fluid
13-b
seemed the most appropriate
acknowledge that she is upset, but don’t dismiss her she obviously came for a reason
14-b
Diphenhydramine is an over the counter medication with side effects including confusion, urinary retention, and mild constipation.
Diphenhydramine causes urinary retention and confusion especially in older adults
15-b
Hot nodules are more likely benign than malignant. Follicular adenomas are the most common cause of solitary nodule. They usually present as a painless mass. The patient’s nodule was found during a routine exam so it is likely a painless mass.
16-d
toxoplasmosis with ring enhancing lesion on radiograph (necrotic abscess)
22-c
39-b
44-d
The reaction goes from Substrate to Product , S to P
Presence of viable sperm in ejaculate. The man must continue to use
contraception (such as a condom) until an examination of his semen reveals that
no sperm are present. The disappearance of sperm from the semen is not
detectable by the patient. Only a specific laboratory and microscopic analysis
of the semen can verify the total lack of sperm, which is the goal of the
vasectomy surgery.
47-c
48-c
age and typical clinical picture
49-d
50-a
which goes to the pericardium and create hemopericardium that is why distant heart sounds and diffuse wet inspiratory cracles
Early diastolic Aortic
regurgitation The
murmur is low intensity, high-pitched, best heard over the left sternal border
or over the right second intercostal space, especially if the patient leans
forward and holds breath in full expiration. The radiation is typically toward
the apex. The configuration is usually decrescendo and has a blowing character.
The presence of this murmur is a good positive predictor for AR and the absence
of this murmur strongly suggests the absence of AR. An Austin Flint murmur is
usually associated with significant aortic regurgitation
9-a
The symptoms described are characteristic of myotonic dystrophy. It is an autosomal dominant trinucleotide repeat disorder. The disease exhibits a highly variable age of onset which decreases with successive generations. Thus, the disease shows at an earlier age in successive generations which is a phenomenon known as anticipation
10-e
low C peptide due to insulin abuse; low blood glucose should suppress insulin in normal pt
Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by treated diabetes patients and rarely occurs in insulin producing tumours. Decreased C-peptide suggests inability to make insulin (such as diabetes Type I.)Insulinoma would have hypoglycemia, high insulin levels, and high C-peptide levels. Type I diabetes would have decreased insulin and c-peptide. The high insulin and low C-peptide (precursor to insulin)suggests that she is ingesting insulin.psych consult?
11-d
At high stringency duplexes form only between strands with perfect one-to-one complementary. Low stringency allows annealing between strands with some degree of mismatch between bases.
So when they renature they reanneal together. High stringency means that the conditions are strict and they won’t accept bad mismatches. So mismatched dna hybridization will be prevented
12-e
mother has oligohydramnios which can be due to problems with development of kidneys or urinary tract which causes little urine production and leads to low amniotic fluid level Baby’s renal system produces amnionic fluid
13-b
seemed the most appropriate
acknowledge that she is upset, but don’t dismiss her she obviously came for a reason
14-b
Diphenhydramine is an over the counter medication with side effects including confusion, urinary retention, and mild constipation.
Diphenhydramine causes urinary retention and confusion especially in older adults
15-b
Hot nodules are more likely benign than malignant. Follicular adenomas are the most common cause of solitary nodule. They usually present as a painless mass. The patient’s nodule was found during a routine exam so it is likely a painless mass.
16-d
toxoplasmosis with ring enhancing lesion on radiograph (necrotic abscess)
cryptococcall
meninge common in aids patients- mening symptoms stiff neck, headache, nausea,
etc.
CMV-viral
especially eye
Pneumocystis
carinii= pneumonia in aids
Toxoplasma-
encephalitis – parasite seen in aids
Treponema
pallidum –neurosyphyllis most common in aids think tabes dorsalis
Image looks
more like encephalitis than meninge. Can
see the dura
17-a
adenomatous polyp
associated with mAPC and risk of adenocarcinoma
A.tubulovillus
adenoma
18-b
Edema is excess fluid outflow into the interstitium commonly caused by
increased capillary pressure, decreased plasma proteins, increased capillary
permeability, and increased interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure
19-c
Mineralcorticoid
increases K loss and feedback inhibition on renin
Orthostatic
hypotension is defined as a reduction of 20
mmhg in systolic and 10 in diastolic.
It occurs in a large number of elderly people. It is a gc which has a lot of mineralcorticoid
activity. Its effects are pretty much
identical to aldosterone. It results in
an increase in ECF and volume and increase in K+ in secretion by increasing the
activity of the N/K ATPase and absorbs
more Na+. Aldostorone stimululates the renin angiotensin system. Thus by
increasing the activity, after aldosterone feedback inhibition will decrease
plasma renin.
20-b
She has symptoms of
PID. On bimanual it is most likely that the mass felt was the fallopian tube
the fallopian tube is
the most common place for pelvic inflammatory disease
21-c
not NADPH
oxidase because hydroxyl radical and hydrogen peroxide are made at normal
levels.
Not
superoxide dismutase because catalyzes conversion of superoxide into oxygen and
hydrogen peroxide…hydrogen peroxide and oxygen are at normal levels.
Not catalase
because catalase does conversion of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen…and those
values are normal.
Not
glutathione peroxidase because (reduces free hydrogen peroxidase to water), and
not involved in opsonization.
Myeloperoxidase
– acts on hydrogen peroxide and chloride ions to produce hypochlorite (OCL-).
We are told that HOCL production is decreased.
After
opsonization, myeloperoxidase and NADPH oxidase are used.
22-c
Nitrates
activate guanylate cyclase and increase cyclic guanine nucleotides. (increase
cyclic GMP levels)
23-e
Pick’s
disease is a frontotemporal neurodegenerative disease…frontal release signs
(grasp, snout)
24-c
Digeorge syndrome. So
mediastinal window (thymus) is narrow. Peripheral lymphocytes will be
decreased. Gamma globulins are normal bec B cells make these, and not affected
by thymus
25-a
Catalase does
destruction of hydrogen peroxide
26-e
180/1000
divided by 120/1500 === 2.25
27-f
leukoplakia
is precursor cancer for squamous cell carcinoma
Kaposi
sarcoma – red or purple patches under the skin
Aphthous
ulcer – canker sore, HSV or autoimmune
Burkitt’s
lymphoma – would be larger
Candida –
white thrush-y, not leukoplakia
Mixed tumor
of parotid gland – roof of mouth
Warthin’s
tumor – painless swelling in lower portion of parotid gland
28-a
Given to
mother of premature babies to prevent hyaline membrane disease(NRDS)
29-d
Has to be on the
right bec that’s what is affected by occlusion and so renin will be released on
right side. Renin will be released by the vein, not artery, bec renin is from
JG cells and will go to vein, not upstream to the artery
30-d
- “Severe 21-hydroxylase deficiency
causes salt-wasting CAH, with life-threatening vomiting and dehydration
occurring within the first few weeks of life. Severe 21-hydroxylase
deficiency is also the most common cause of ambiguous genitalia due to prenatal virilization
of genetically female (XX) infants.
- Moderate 21-hydroxylase deficiency is referred to as
simple virilizing CAH; and typically is recognized as
causing virilization of prepubertal children.
- Still milder forms of 21-hydroxylase deficiency are referred to as non-classical CAH and can cause androgen effects and infertility in adolescent and adult women.
31-d
The
classic childhood case of HUS occurs after bloody diarrhea caused by E. coli O157:H7, a strain of E. coli that expresses verotoxin (also called Shiga toxin). The toxin enters the bloodstream, attaches to renal
endothelium and initiates an inflammatory reaction leading to acute renal failure (ARF)
and disseminated
intravascular coagulation (DIC). The fibrin
mesh destroys red blood cells and
captures thrombocytes, leading to a decrease of
both on complete blood count. The
usual age of onset is between 2 and adolescence
32-d
Cleft lip and palate is nonsyndromic, so multifactorial
33-a
Candida is common in diabetes. The rest are std’s. also, the image is definitely candida
34-h
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (microangiopathic hemolytic
anemia, acute renal failure and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia).) we would
see the narrowing of the capillary wall by fibrin deposition.
32-d
Cleft lip and palate is nonsyndromic, so multifactorial
33-a
Candida is common in diabetes. The rest are std’s. also, the image is definitely candida
34-h
BSE is a prion disorder (protein, infectious). So not
DNA, RNA, but it is protein
35-a
Arginine is necessary for NO production
36-e
Alcoholics get portal htn, leading to esoph varices,
which can rupture.
37-a
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperparathyroidism
38-d
Lots of SIGECAPS
39-b
Salycylism
40-b
Not a straight line, but still a positive correlation
41-e
Not a straight line, but still a positive correlation
41-e
FDA
REGULATES BOTH Efficacy and safety of drugs
Preclinical animal studies:
Results include Data on
1. organ
system toxicity
2. mutagenic<AMES test> and carcinogenic potential
3. effect
on reproductive performance
4. effectiveness
of drug
clinical
testing:
after
IND exemption
Phase 1: safety:
The drug is
tested in a few healthy volunteers . pharmacokinetic properties
Phase 2: does it
work/effectiveness
100/more pts in comparision with placebo/+control
Single/double blinded
Phase 3:how well does it
work/common side effects
The drug is
typically tested in 1000/ more pts , in comparision with placebo and positive
control usually double-blind
Phase 4:follows a NDA, a request for marketing
approval, and involves pms of adverse effects.
Quantifies common side effects,reveal less common and
more severe toxicities that could warrant withdrawal
42-d
First of all,
most of the bacterial polysaccharides are T-lymphocyte independent antigens.
Antipolysaccharide
immune response
is characterised by lack of T-lymphocyte memory, isotype restriction and
delayed ontogeny.
Children below 2
years of age and elderly respond poorly to polysaccharide antigens. Secondly,
the wide structural heterogeneity among the polysaccharides within and between
species is also a problem. Thirdly, some bacterial polysaccharides are poor immunogens
in humans due to their structural similarities with glycolipids and
glycoproteins present in man. The T-lymphocyte independent nature of a
polysaccharide may be overcome by
conjugating the native or
depolymerised polysaccharide to a protein carrier. Such neoglycoconjugates have been proven to be
efficient in inducing T-lymphocyte dependent immunity and to protect both
infants as well as elderly from disease. Another approach to circumvent the
T-lymphocyte independent property of polysaccharides is to select peptides
mimicking the immunodominant structures. Several examples of such peptides have been described.
B lymphocytes recognize 5-6 amino acids in case of
protein / 4-5 hexose units of polysacc
T lym recognize 10-20 amino acids in length on surface
of MHC of APC
TH cells necessary for immunolo memory
So H. inf type b coupled to protein – N. men OMP /
diphtheria toxoid
Polysacch capsule vaccines 0f N.men and S.pneu not
administered with protein component
43-b

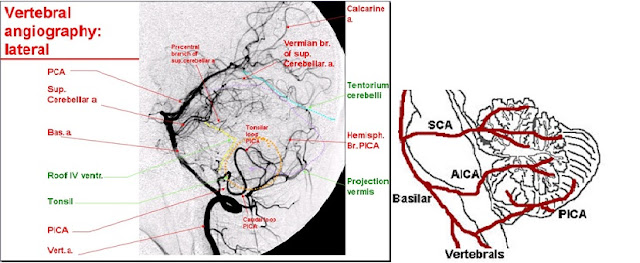
first step: which artery is
involved? as seen in angiogram this artery arise form proximal portion of
basilar artery, so this is anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA).
second step: which structures
supply AICA. AICA supplies the caudal lateral pontine tegmentum, and inferior
surface of the cerebellum.
third step: choose from given
answer options which is characteristic for cerebellar dysfunction. a, d, e are
characteristic for hemisphere
c. is characteristic for basal ganglia
only b. ataxic limb
movements left, which is the correct answer44-d
The reaction goes from Substrate to Product , S to P
When ∆ G is –, the reaction goes in direction from S to P
When ∆ G is + , the reaction goes from P to S
v-w-x-y-z
the reason being that G0 is spontaneous when it is
negative.. these reacations are reversible. so y-->z is +5.7 so then
z--->y is -5.7 meaning THAT IS THE MOST SPONTANEOUS REACTION and so you
would accumulate Y..
if G is negative number reaction goes forward
if G is a positive number reaction cant occur and
requires energy
so now from the values given u can easily go from v -w
w-x ,little energy is required
now x will be spontaneously converted to y becoz G is
negative
but y-z requires a lot oh energy .......so y will
accumulate.
- delta G means that reaction is favorable. More -
delta G, more favorable reaction. +delta means that reaction is unfavourable.
More + delta G, more unfavourable the reaction. So, V->W reaction (deltaG
-4,0) very favourable, it will lead to accumulation of large quantitie of
product W.
In the presence of large amount of W, second little
unfavourable reaction (deltaG +0,4)
W->X will proceed.
X->Z reaction (deltaG -3,5) is also very
favourable, and results in accumulation of product Y.
last reaction (deltaG +5,7) very unfavourable. so it
would not occur at all.
So correct answer is D. Y will accumulate in the
largest amount at equilibrium.
45-a
How many fatal recreational cases (1) to all
recreational cases( 12 )
Case Fatality is number of deaths/ number of diagnosed
patients 1/12
46-d
48-c
age and typical clinical picture
49-d
50-a
which goes to the pericardium and create hemopericardium that is why distant heart sounds and diffuse wet inspiratory cracles
Pain radiates to the back , long history of poorly
controlled hypertension
Blood pressure
difference on R and L hands
Pseudohypotension (falsely low
blood pressure measurement) may occur due to involvement of the brachiocephalic
artery (supplying the right arm) or the left subclavian artery (supplying the
left arm).
This is really good
ReplyDeletedo you have the explanations for other NBMES?
Thanks, it's really good.
ReplyDeleteThanks, for sharing this informative post with us. This post is helpful for medical students. Now, i share this post with group of medical students who studies at All Saints University College Of Medicine. This university offer basic science to MD Degree program without taking any entrance exam and also offer scholarship to medical students.
ReplyDelete